Tensor Object Detection 🕵️♀️
The task of TensorObjectDetection involves the identification, categorization, and location of individual objects or
specific features within the entire tensor system.
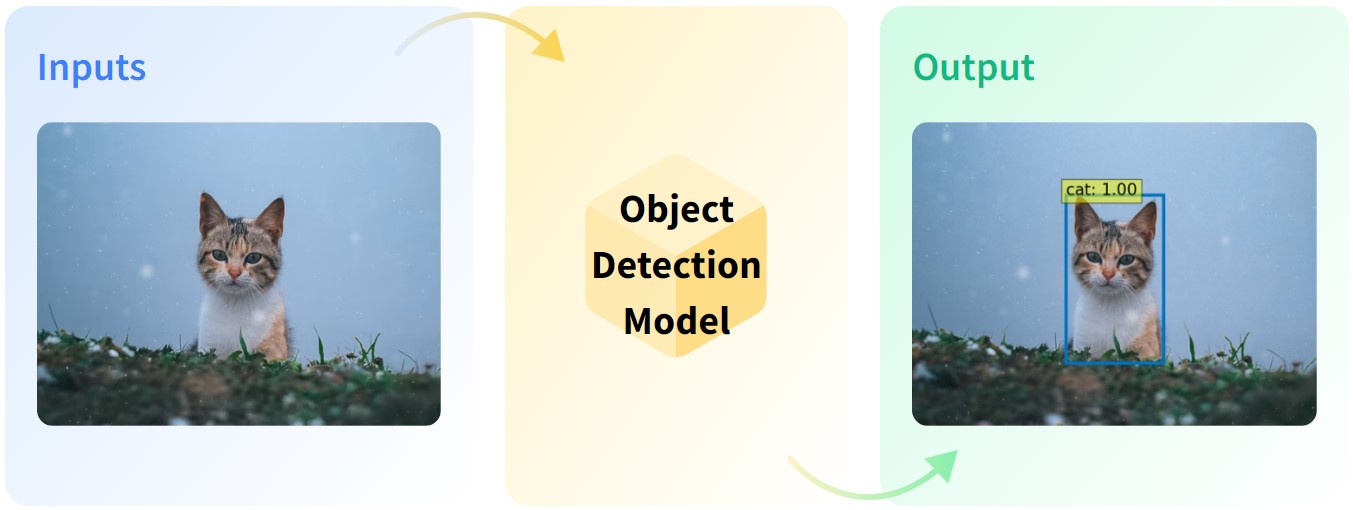
📌 Inputs:
- SampleTensor [input]:
- A tensor ranging from 1D to 5D.
- SampleTensor [target]: (optional)
- A 2D tensor contains bounding boxes and category labels for each object. The bounding boxes are formatted
as
(class_*, centroid_*, length_*). For instance, simple car detection on a 3D tensor can be of the form [[0, 10, 20, 5, 5], ...]. Where the first number is theclassof the object, the second number is thexcoordinate of the centre of the object, the third number is theycoordinate of the centre of the object, the fourth number is thewidthof the object, and the fifth number is theheightof the object.
- A 2D tensor contains bounding boxes and category labels for each object. The bounding boxes are formatted
as
- SampleTensor [extra]: (optional)
- Additional tensors that may assist in exploratory data analysis or the training process.
🛠️ Use Cases:
- Urban Planning and Monitoring: Detecting and monitoring buildings, roads, and other infrastructures.
- Environmental Conservation: Identifying changes in land cover, monitoring deforestation, and water bodies.
- Disaster Response: Locating affected areas during floods, forest fires, or after other natural calamities.
- Agriculture: Monitoring crop patterns, field conditions, and estimating potential yield.
- Defense: Recognizing specific structures, vehicles, or other samples of interest for national security.
🔍 Example:
import mlstac
name = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/mlstac/tensor_object_detection_demo.json"
dataset = mlstac.dataset(name, streaming=True, framework="torch")
print(next(iter(dataset)))
# Output example:
# {'input': tensor([[[[...]]]]), 'target': tensor([[0, 10, 20, 5, 5], ...])}